
Technology Due Diligence in M&A: Hidden Risks Your Team Missed
Technology due diligence in mergers and acquisitions often determines the difference between success and failure. Between 40-60% of expected synergies in M&A deals are directly linked to IT integration success, yet technology integration issues account for approximately 30% of failed mergers. As CEO of CyberMedics, I’ve witnessed firsthand how overlooked technical details can derail otherwise promising acquisitions.
Throughout my years conducting technology due diligence, I’ve seen a concerning pattern where critical risks remain hidden until after the deal closes. Companies that conduct comprehensive technology due diligence are 28% more likely to achieve their projected synergies and 32% more likely to retain key technical talent post-acquisition. Despite this, a staggering 83% of IT leaders express concerns about limitations imposed by outdated technologies during integration.
The financial impact is equally significant. According to the Ponemon Institute, enterprises waste up to $5 million annually due to inefficiencies linked to poorly integrated systems, while legacy systems can inflate operational costs by up to 30%. Furthermore, without a thorough IT due diligence strategy, acquiring companies may unknowingly inherit technical debt, security gaps, or inefficient systems that lead to integration challenges, regulatory fines, and operational disruptions.
At CyberMedics, we’ve developed our proprietary CyberProcess™ specifically to uncover these hidden risks before they become costly problems. Our methodical approach combines business process analysis, human-centric design, and structured change management to identify integration challenges that standard checklists miss. Using a structured technology due diligence checklist increases the likelihood of identifying critical issues by over 60% compared to ad-hoc approaches.
In this article, I’ll share the most commonly overlooked technical risks in M&A transactions and provide actionable insights on how to identify and mitigate them before they compromise your deal’s value.
Key Takeways
Section | Key Takeaways |
Introduction | Technology due diligence in M&A often determines success or failure. Many deals fail due to overlooked IT risks that could have been uncovered with the right expertise and approach. |
Why Technology Due Diligence Often Misses Critical Risks | Lack of technical expertise, overreliance on vendor documentation, and underestimating IT complexity lead to missed risks. These blind spots result in post-close surprises and inflated costs. |
Hidden Risk #1: Legacy Systems and Technical Debt | Legacy platforms, undocumented code, and patch backlogs represent significant hidden liabilities. These issues increase security vulnerabilities, operational inefficiencies, and integration costs. |
Hidden Risk #2: Poor Integration Readiness | Siloed systems, lack of API standardization, incompatible data models, and missing middleware complicate integration, delay timelines, and erode synergy value. |
Hidden Risk #3: Compliance and Security Gaps | Non-compliance with GDPR, HIPAA, PCI, and unpatched vulnerabilities expose acquirers to regulatory penalties and security breaches. Poor access control magnifies risks. |
Hidden Risk #4: Talent and Knowledge Concentration | Overdependence on key personnel, lack of succession planning, and unclear IP ownership can stall integration and create operational and legal challenges if not addressed. |
Conclusion | Identifying and quantifying these hidden risks early enables accurate valuation and smoother integration. CyberMedics’ CyberProcess™ provides a structured methodology to uncover these risks and protect M&A investments. |
Why Technology Due Diligence Often Misses Critical Risks
The statistics tell a sobering story: nearly half (47%) of M&A deals fail primarily because of IT challenges. In my experience leading CyberMedics through hundreds of technology assessments, this failure rate stems not from a lack of effort, but from fundamental blindspots in the due diligence process itself.
Lack of Technical Expertise in Deal Teams
Deal teams consistently prioritize financial metrics and operational synergies while relegating technology to an afterthought. Shockingly, only 56% of decision-makers even consider IT issues during the due diligence phase. This oversight occurs because most M&A professionals come from financial or legal backgrounds with limited technical fluency.
Without dedicated technical expertise, deal teams often mistake functional demos for scalable systems. At CyberMedics, we once reviewed an acquisition target whose demo environment performed flawlessly, yet collapsed under real-world user volumes. Had the buyer proceeded without our assessment, they would have discovered this limitation only after investing millions.
Additionally, many organizations find their internal IT teams lack sufficient bandwidth to handle acquisition challenges. These teams are already stretched thin with daily responsibilities, and furthermore, many IT professionals lack M&A experience, making it difficult for them to provide strategic input during critical evaluation phases.
Overreliance on Vendor Documentation
A second critical mistake I frequently encounter involves excessive trust in vendor-provided documentation. Throughout my tenure at CyberMedics, I’ve seen countless instances where surface-level vendor documentation masked significant underlying issues.
Organizations that rely heavily on vendors but lack sufficient visibility into their networks expose themselves to substantial risks. Many companies fail to track vendor risks against internal policies and certifications, ultimately resulting in operational issues that surface post-acquisition.
Consider this: outsourcing business activities to a vendor does not include outsourcing compliance responsibility. The acquiring company bears the burden of conducting thorough vendor due diligence. Our CyberProcess™ methodology specifically addresses this by performing independent verification rather than accepting documentation at face value.
Underestimating the Complexity of IT Environments
Perhaps the most pervasive issue stems from underestimating the intricate nature of modern IT landscapes. IT separation typically consumes between 40-60% of the total separation budget in M&A transactions. This substantial allocation reflects the true complexity that many deal teams initially dismiss.
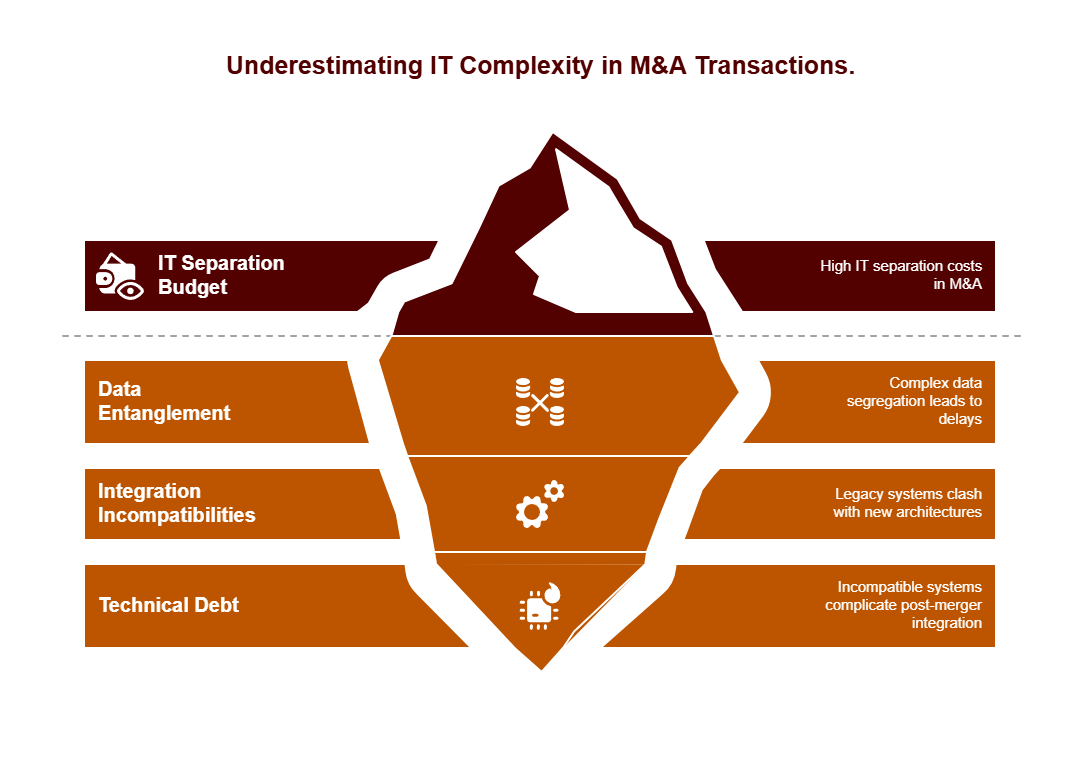
When evaluating potential acquisitions, I’ve consistently identified these commonly overlooked factors:
- Data entanglement issues – Many buyers discover too late that data segregation is significantly more complex than anticipated, leading to project delays and compliance problems with regulations like GDPR.
- Integration incompatibilities – For example, a bank acquiring a payment company might overlook that its legacy core systems are fundamentally incompatible with the modular microservices architecture of the acquired payment app.
- Technical debt accumulation – Post-merger integration is often complicated by technical debt in the form of incompatible systems, undocumented code, and lack of standardized processes.
Essentially, the complexity of vendor relationships increases as the vendor base grows. Monitoring these relationships becomes increasingly challenging when companies use undefined, fragmented, and decentralized vendor monitoring systems that are both time-intensive and difficult to scale.
Through our CyberProcess™ methodology at CyberMedics, we’ve developed specialized assessment techniques that look beyond surface-level compatibility to identify these hidden integration barriers. By combining business process analysis with human-centric design principles, we uncover integration challenges that standard checklists invariably miss.
Hidden Risk #1: Legacy Systems and Technical Debt
Legacy systems and technical debt represent the most expensive and commonly overlooked risks we encounter in technology due diligence in mergers and acquisitions. As we’ve witnessed repeatedly at CyberMedics, these issues often remain invisible during standard assessments yet become glaringly obvious post-acquisition.
According to McKinsey, technical debt consumes up to 40% of an organization’s entire technology estate. More alarmingly, analysis shows that 31% of acquired codebases are riddled with technical debt. This hidden burden inflates acquisition costs, undermines scalability, and can derail integration efforts.
Unsupported Platforms and End-of-Life Software
One startling statistic that continues to surprise my clients: 70% of software used by Fortune 500 companies was developed over 20 years ago. This poses immediate security concerns since End-of-Life (EOL) software no longer receives critical security updates.
Through our CyberProcess™ methodology, we frequently uncover unsupported platforms that pose substantial risks:
- Security vulnerabilities that cannot be patched
- Compliance violations with frameworks like PCI DSS and HIPAA
- Operational inefficiencies costing approximately $3 million annually per organization
I recently led a technical due diligence engagement where we discovered a target company running financial systems on platforms that had reached EOL five years prior. Without patches or vendor support, these systems had become what I call “security sieves” – riddled with vulnerabilities that cybercriminals actively scan for.
Moreover, outdated banking legacy systems, become “easily exploitable weaknesses in the financial sector”. Consequently, organizations must factor substantial modernization costs into any deal involving legacy technology.
Custom Code with No Documentation
Undocumented code represents another costly liability that I consistently uncover during technical due diligence. Our proprietary CyberProcess™ specifically looks for warning signs including:
- Architecture documentation that is missing or severely outdated
- Code lacking meaningful comments
- Configuration management that is poorly documented
In one acquisition we assessed, knowledge was concentrated among just three senior developers. Following the acquisition, two departed, leaving the buyer with systems nobody fully understood. Ultimately, they abandoned integration plans altogether, forfeiting projected synergies worth millions.
KPMG reports that nearly 60% of organizations cite legacy systems as barriers to achieving strategic goals, with 45% of IT leaders stating these systems specifically hindered their merger and acquisition efforts.
Deferred Maintenance and Patch Backlogs
Patch backlogs constitute the third critical component of technical debt I routinely uncover. According to IDC, 47% of IT leaders cite excessive technical debt as a major factor driving IT budget overruns.
Throughout my career conducting technical due diligence, I’ve observed how security vulnerabilities in unpatched systems create exposure that grows exponentially over time.
At CyberMedics, we assess deferred maintenance by examining:
- Backlog of security patches and critical updates
- Frequency of production incidents
- Extensive workarounds for core functionality
Technical debt exceeding 20-25% of overall development effort typically indicates systematic underinvestment. Subsequently, this signals potential future liabilities that must be factored into valuation and integration planning.
Identifying these hidden risks early in the technology due diligence process allows us to accurately quantify remediation costs. Otherwise these costs emerge unexpectedly post-acquisition, eroding anticipated deal value and derailing integration timelines.
Hidden Risk #2: Poor Integration Readiness
Poor integration readiness represents one of the most insidious risks in technology due diligence in mergers and acquisitions. Throughout my career at CyberMedics, I’ve witnessed firsthand how integration problems can silently sabotage even the most financially sound transactions.
Siloed Systems Across Business Units
In our experiences conducting technical due diligence, fragmented systems create integration nightmares. Warning signs I routinely identify include:
- Heavy reliance on manual data transfers between systems
- Critical business information trapped in personal spreadsheets
- Inconsistent data definitions across departments
These issues typically extend integration timelines and increase costs, often severely undermining projected synergies. Indeed, our CyberProcess™ methodology specifically examines how these silos echo organizational structures.
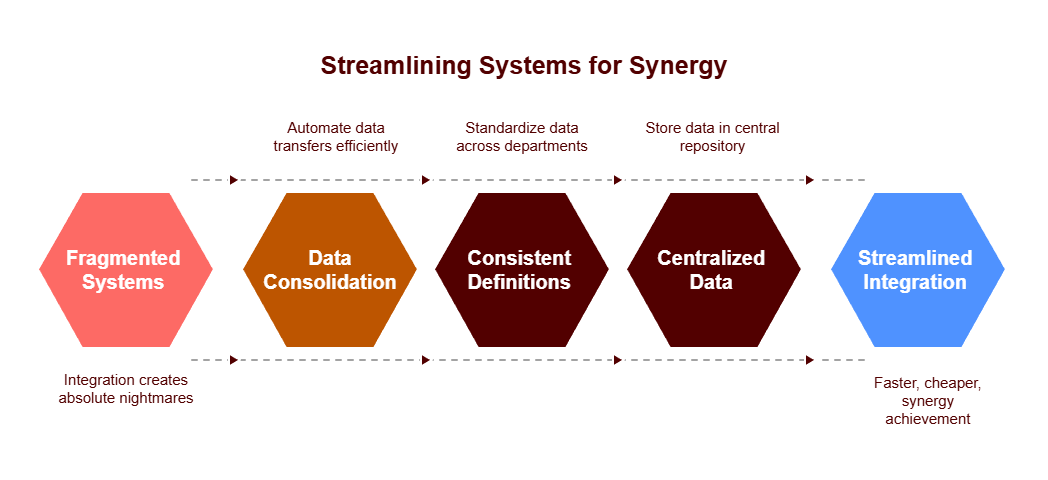
One particular acquisition I assessed involved a company where each business unit operated in complete isolation. As a result, the timeline for integration doubled, wiping out nearly 30% of the anticipated synergy value. This outcome was entirely predictable—and preventable—with proper assessment.
Lack of API Standardization or Middleware
Effective integration requires standardized communication channels between systems. Nevertheless, we frequently discover that organizations underestimate middleware complexity. At this point in the technical due diligence process, we focus on identifying whether the target company utilizes:
Middleware solutions that enable seamless communication across ERP, CRM, and transactional systems. First, we evaluate how effectively these solutions synchronize real-time data. Second, we determine whether they can accommodate increasing data volumes.
In fact, through our CyberProcess™ assessment, we’ve saved clients millions by identifying middleware limitations early. One pharmaceutical client nearly discovered post-acquisition that their target had no standardized APIs—a revelation that would have added 18 months to their integration timeline.
Incompatible Data Models and Schemas
The third critical integration barrier lies in data compatibility challenges. Companies frequently struggle with disparate data sources maintaining information in separate systems and incompatible formats.
Our methodology specifically evaluates:
- Disparate data definitions and formats across systems
- Inconsistencies in terminology for identical concepts
- Limited connectivity between data relationships
Ready checkpoints (RCPs) incorporated into integration plans help identify these issues, pressure-testing operational activities. Such assessments can galvanize transaction teams toward a common goal of enabling business continuity.
Cloud-based platforms, standardized data structures, and systems with open APIs make m&a technology integration far more manageable and reduce the timeline to achieve synergies. Through CyberMedics’ proprietary approach, we’ve consistently helped clients navigate these integration challenges before they derail acquisition value.
Hidden Risk #3: Compliance and Security Gaps
Compliance and security gaps form a treacherous minefield in technology due diligence that I’ve seen derail numerous acquisitions. Throughout my career at CyberMedics, I’ve observed how regulatory non-compliance often remains hidden until post-acquisition audits reveal costly violations.
GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI Non-Compliance
Regulatory mismatches between companies create immediate legal exposure upon acquisition. For instance, a European company inheriting systems that are CCPA-compliant but not GDPR-compliant faces significant legal risks. Unlike CCPA, which merely requires opt-out mechanisms, GDPR demands explicit consent before storing consumer data.
Our CyberProcess™ specifically examines compliance gaps across these critical frameworks:
- HIPAA – Protecting patient health information with penalties up to $1.5 million per incident
- PCI DSS – Securing payment card data with fines ranging from $5,000 to $100,000 monthly
- GDPR – Governing all personal data with potential fines reaching millions
One manufacturing client nearly acquired a company whose PCI non-compliance would have triggered immediate penalties exceeding $300,000.
Unpatched Vulnerabilities in Legacy Systems
Unaddressed security flaws create immediate exposure in acquisitions. Alarmingly, 60% of breach victims were compromised through known vulnerabilities they simply hadn’t patched.
Through our technical assessments, I frequently uncover “legacy grenades” – systems with vulnerabilities that explode after the deal closes. The 2017 Equifax breach exemplifies this risk, where unpatched systems exposed 148 million records.
Hence, our CyberProcess™ methodology specifically identifies systems with unpatched vulnerabilities and inherited security weaknesses that existed pre-acquisition.
Lack of Role-Based Access Controls
Proper access management prevents unauthorized data exposure. Yet 62% of organizations consider role-based access critical, though only 54% feel confident implementing it effectively.
I consistently find companies relying on outdated access management methods—manually tracking users and entitlements—an approach that’s both costly and risky. Furthermore, this creates immediate security exposure during integration when combining user populations.
Through CyberProcess™, we identify access control gaps early, implementing the principle of least privilege to ensure users access only what they need. This approach is particularly valuable for seasonal workers, contractors, and throughout M&A transitions.
Hidden Risk #4: Talent and Knowledge Concentration
The human element represents perhaps the most overlooked dimension in technology due diligence in mergers and acquisitions. Throughout my career at CyberMedics, I’ve witnessed how knowledge concentration issues can silently undermine acquisition value long after technical systems have been integrated.
Key Person Dependencies in IT Teams
Excessive reliance on key individuals creates substantial operational risk that few acquirers properly quantify. Based on our assessments, key person dependencies typically manifest when knowledge accumulates primarily among experienced engineers, creating what I call “knowledge islands”. These situations often lead to potential downtime or stagnated product advancement if those knowledgeable engineers depart post-acquisition.
One financial services client I advised was blindsided when three critical developers resigned shortly after acquisition announcement. Their departure effectively halted integration efforts for six months. Critically, 35% of global technology leaders report insufficient AI expertise as a primary challenge in developing organizational capabilities.
No Succession or Knowledge Transfer Plans
Absent succession planning represents a time bomb in technical due diligence. Alarmingly, 41% of companies lack succession plans for Chief Information Security Officer roles. Furthermore, almost a third of cybersecurity professionals consider leaving the profession occasionally (21%) or regularly (9%) due to stress factors.
Through our CyberProcess™ methodology, we specifically evaluate:
- Documentation completeness across critical systems
- Knowledge distribution across technical teams
- Formalized succession planning for key technical roles
Institutional knowledge preservation becomes particularly vital during m&a technology integration. Without systematic identification of critical roles and proactive successor development, businesses risk significant knowledge gaps.
Contractor Reliance Without IP Ownership
IP ownership ambiguity creates substantial mergers and acquisitions risk. Many companies I’ve evaluated during technology due diligence rely heavily on contractors without proper IP agreements.
Effective agreements must include “commissioned for use” provisions ensuring any contractor-created IP becomes company property. Likewise, for employees, “work made for hire” provisions remain essential. Without these protections, critical intellectual property ownership remains vulnerable.
At CyberMedics, our technical due diligence process specifically examines employee and contractor agreements to verify proper IP assignment provisions exist, protecting acquirers from post-close IP disputes that could jeopardize core business functionality.
Conclusion
Throughout my years directing technology due diligence assessments, I’ve witnessed firsthand how these four critical risk areas can destroy acquisition value when overlooked. Legacy systems and technical debt often create immediate financial burdens, while integration challenges extend timelines and erode projected synergies. Similarly, compliance gaps expose companies to substantial regulatory penalties, and knowledge concentration issues can paralyze operations when key personnel depart.
The financial implications remain staggering. Organizations waste millions annually on inefficiencies from poorly integrated systems while simultaneously increasing their exposure to security breaches and compliance violations. After all, technical due diligence isn’t merely about checking boxes—it requires deep expertise to uncover issues that standard assessments miss.
My team at CyberMedics developed our CyberProcess™ methodology specifically to address these hidden risks before they compromise deal value. This approach combines rigorous technical assessment with business process analysis to identify integration barriers that would otherwise remain invisible until after closing. Consequently, we help acquirers quantify remediation costs accurately and factor them into valuation discussions.
The patterns I’ve observed across hundreds of assessments confirm that companies who invest in comprehensive technology due diligence significantly outperform those who treat IT as an afterthought. They achieve synergies faster, retain technical talent more effectively, and avoid costly surprises during integration.
Undoubtedly, technical debt, integration barriers, compliance gaps, and knowledge concentration represent the most expensive yet commonly overlooked risks in M&A transactions. These issues demand specialized expertise to identify and mitigate. Assess your technology risk with experts—contact CyberMedics to evaluate your current and target systems with our proven CyberProcess™ to gain actionable insights and protect your investment. The difference between successful integration and a failed merger often comes down to what your team discovers before signing—not after.
FAQs
Q1. What are the most common hidden risks in technology due diligence for M&A?
The most common hidden risks include legacy systems and technical debt, poor integration readiness, compliance and security gaps, and talent and knowledge concentration issues. These risks often go undetected during standard assessments but can significantly impact the success of a merger or acquisition.
Q2. How does technical debt affect M&A transactions?
Technical debt can consume up to 40% of an organization’s technology estate and inflate acquisition costs. It can undermine scalability, derail integration efforts, and lead to security vulnerabilities. Identifying and addressing technical debt early in the due diligence process is crucial for accurate valuation and successful integration.
Q3. Why is integration readiness important in technology due diligence?
Integration readiness is critical because poor integration can sabotage even financially sound transactions. Issues like siloed systems, lack of API standardization, and incompatible data models can extend integration timelines, increase costs, and undermine projected synergies. Assessing integration readiness helps prevent these problems.
Q4. What are the potential consequences of overlooking compliance and security gaps?
Overlooking compliance and security gaps can lead to immediate legal exposure, financial penalties, and increased vulnerability to data breaches. Non-compliance with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS can result in fines ranging from thousands to millions of dollars. Unpatched vulnerabilities in legacy systems also pose significant security risks.
Q5. How does talent and knowledge concentration impact M&A success?
Excessive reliance on key individuals creates substantial operational risk. If these key personnel depart post-acquisition, it can lead to potential downtime or stagnated product advancement. Lack of succession planning and knowledge transfer can create significant knowledge gaps, potentially paralyzing operations during integration.
